Ligamentum Flavum Thickening | Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy, also known as ligamentum flavum thickening, is a health condition related to the spine and lower back. Failure of percutaneous remodeling of the ligamentum flavum and lamina for neurogenic claudication. Thickening of the ligamentum flavum increases with age in the lower lumbar levels and in patients with chronic back pain. Introductionas the ligamentum flavum (lf) covers most of the posterolateral part of the lumbar spinal canal, its thickening can be attributed to the development of lumbar canal encroachment. Thickening of the ligamentum flavum is often attributed to the buckling of a normal ligamentum flavum when the disk at that level narrows.
Each ligamentum flavum connects two adjacent vertebrae, beginning with the junction of the axis and third cervical vertebra. Measurements of ligamentum flavum thickening at lumbar spine using mri. Uncertainty exists as to whether this can. New observations and their surgical importance. As the ligamentum flavum (lf) covers most of the posterolateral part of the lumbar spinal canal, its thickening can be attributed to the development of lumbar canal encroachment.

Ligamentum flavum thickening is a pathological and neurodegenerative condition that affects the ligamentum flavum — the spinal ligaments that connect the laminae to the nearby vertebrae. Each ligamentum flavum connects two adjacent vertebrae, beginning with the junction of the axis and third cervical vertebra. This condition is usually found in patients suffering from a. This is the result of segmental. If severe, it can be associated with central canal stenosis. Ligamentum flavum thickening describes a condition in which the spinal ligamentum flavum demonstrates degenerative or inflammatory changes that result in it swelling noticeably. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is a condition in which the ligamentum flavum (lf) thickens due to stresses placed on. This study examined whether ligamentum flavum thickening is due to tissue hypertrophy or buckling and whether it is related to disc degeneration, and it examined the correlations between the thickness. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is also known as ligamentum flavum thickening. This condition involves the ligamentum flava, or aptly named yellow. In some cases, ligamentum flavum hypertrophy or ligamentum flavum thickening may also result in spinal stenosis which may contribute further to the pain that an individual suffers due to. Assessment of traumatic brain injury online course: What is ligamentum flavum hypertrophy?
Thickening of the ligamentum flavum increases with age in the lower lumbar levels and in patients with chronic back pain. Introductionas the ligamentum flavum (lf) covers most of the posterolateral part of the lumbar spinal canal, its thickening can be attributed to the development of lumbar canal encroachment. As the ligamentum flavum (lf) covers most of the posterolateral part of the lumbar spinal canal, its thickening can be attributed to the development of lumbar canal encroachment. If severe, it can be associated with central canal stenosis. In this condition, the ligament.

Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is also known as ligamentum flavum thickening. In this condition, the ligament. Is it buckling or enlargement? New observations and their surgical importance. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is also commonly known as ligamentum flavum thickening. The anatomy of the human lumbar ligamentum flavum: Assessment of traumatic brain injury online course: Introductionas the ligamentum flavum (lf) covers most of the posterolateral part of the lumbar spinal canal, its thickening can be attributed to the development of lumbar canal encroachment. Measurements of ligamentum flavum thickening at lumbar spine using mri. This replacement with collagen causes the ligamentum flavum to thicken (up to 10 times its normal width. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is a condition in which the ligamentum flavum (lf) thickens due to stresses placed on. This study examined whether ligamentum flavum thickening is due to tissue hypertrophy or buckling and whether it is related to disc degeneration, and it examined the correlations between the thickness. Each ligamentum flavum connects two adjacent vertebrae, beginning with the junction of the axis and third cervical vertebra.
What is ligamentum flavum hypertrophy? Severe bilateral facet arthrosis and ligamentum flavum. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy refers to the ligament becoming less elastic due to thickening it means that the ligamentum flavum is overgrown or split in two. This study examined whether ligamentum flavum thickening is due to tissue hypertrophy or buckling and whether it is related to disc degeneration, and it examined the correlations between the thickness. In some cases, ligamentum flavum hypertrophy or ligamentum flavum thickening may also result in spinal stenosis which may contribute further to the pain that an individual suffers due to.
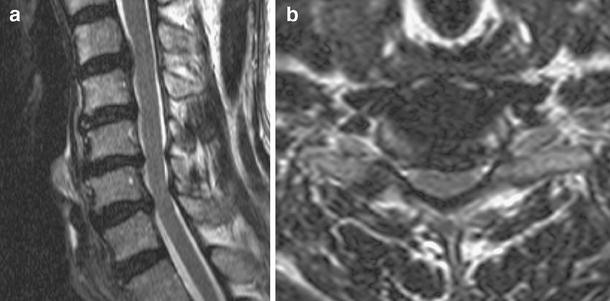
Uncertainty exists as to whether this can. This replacement with collagen causes the ligamentum flavum to thicken (up to 10 times its normal width. This condition is usually found in patients suffering from a. Introductionas the ligamentum flavum (lf) covers most of the posterolateral part of the lumbar spinal canal, its thickening can be attributed to the development of lumbar canal encroachment. This study examined whether ligamentum flavum thickening is due to tissue hypertrophy or buckling and whether it is related to disc degeneration, and it examined the correlations between the thickness. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is also known as ligamentum flavum thickening, or occasionally, as ligamentum flavum stenosis. The key molecules and mechanisms responsible for hlf remain unclear. The anatomy of the human lumbar ligamentum flavum: Ligamentum flavum, facet joint, intervertebral disc, end plate degeneration, mri. Pathology it is thought to be mostly from fibrosis. What is ligamentum flavum hypertrophy? As the ligamentum flavum (lf) covers most of the posterolateral part of the lumbar spinal canal, its thickening can be attributed to the development of lumbar canal encroachment. Thickening of the ligamentum flavum is often attributed to the buckling of a normal ligamentum flavum when the disk at that level narrows.
Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is also known as ligamentum flavum thickening, or occasionally, as ligamentum flavum stenosis ligamentum flavum. As the ligamentum flavum (lf) covers most of the posterolateral part of the lumbar spinal canal, its thickening can be attributed to the development of lumbar canal encroachment.
Ligamentum Flavum Thickening: Measurements of ligamentum flavum thickening at lumbar spine using mri.

No comments:
Post a Comment